Describe Three Functions of the Skin
The skin has three main functions. For each function describe the structures in the skin that contribute to that function.
The skin acts as a protective barrier from.

. Functions of the skin. - lies beneath dermis. The skin is broken up into 3 different layers the epidermis or top layer dermis and subcutaneous layer.
Name three 3 functions of the skin. The skin has three main functions. Wounding affects all the functions of the skin.
The Malpighian layer produces the skins pigmentation and protects it against the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation. The skin has three main functions. The middle dermis is responsible for supporting and strengthening the skin.
Mechanical thermal and other physical injury. Protection UV mechanical chemical thermal plus is a physical barrier to invasion 2. The skin performs six primary functions which include protection absorption excretion secretion regulation and sensation.
The cell membrane engulfs a particle or substance drawing it into the cell in a vesicle B. Briefly describe three 3 functions of the skin. Include what section or parts of the skin may contribute to the function what is the significance of having these functions for our body.
Protection regulation and sensation. Figure 533 Aging. It serves as a protective barrier to the internal organs and structures of the body C.
Mechanical impacts and pressure variations in temperature micro-organisms radiation and chemicals. The skin provides protection from. Explain the Features of the Hypo Dermis.
The skin is broken up into 3 different layers the epidermis or top layer dermis and subcutaneous layer. Helps regulate body temperature B. Janet Ramsden The accessory structures also have lowered activity generating thinner hair and nails and reduced amounts of sebum and sweat.
It protects us from external elements regulates the body temperature by releasing water in the form of sweat and allows sensations such as touch heat and cold. - contains nerve endings that. Each of these layers performs important roles in keeping our body healthy.
Generally skin especially on the face and hands starts to display the first noticeable signs of aging as it loses its elasticity over time. Within this it performs several important and vital physiological functions as outlined below Graham-Brown and Bourke 2006. Metabolic Subcutaneous fat as energy VitD synthesis.
List functions of skin and relate them to its structures arrow_forward Describe how the skin contributes to the regulation of body temperature storage of blood protection sensation excretion and absorption and synthesis of vitamin D. Protection regulation and sensation. The primary function of the skin is to act as a barrier.
The skin acquires an area of 20 square feet on our body surface. The outermost epidermis is responsible for producing new skin cells protecting the body from unwanted substances and retaining moisture to keep the skin well hydrated. Each of these layers performs important roles in keeping our body healthy.
The dermis connects the epidermis to the hypodermis and provides strength and elasticity due to the presence of collagen and elastin fibers. For each function describe the structures in the skin that contribute to that function. Match the movements into and out of the cell on the left with their descriptions on the right.
Name three 3 functions of the skin. Movement down a concentration gradient. Sensation Rc for touch pressure pain temp 4.
The skin consists of layers each containing important elements that serve to protect the body against harm. Describe and name three functions of the skin there are more than 3 related functions BUT only include three here. The skin performs six primary functions which include protection absorption excretion secretion regulation and sensation.
The skin is an organ of protection. It helps keep the skin moisturized and nourishes the epidermis. - anchors the skin to underlying structures.
Keratinocytes tough Sebum lubricant and anti bacterial and Mucous Secretion from the skin from the acid mantle which aide in creating a healthy environment Pigment melanin protects from Ulta-Violet UV ray damage adipose tissue provides protection of underlying structure Great protection as long as skin stays in one piece. The skin has the ability to absorb transdermal medications. The epidermis consists of several layers The topmost layer consists of dead cells that shed periodically and is progressively replaced by cells formed from the basal layer.
What are the main functions of skin to human body. The skin has six primary functions that help maintain its homeostasis. - adipose tissue fatty tissue cushions and insulates.
1 sample diffusion 2 facilitated diffusion 3 filtration 4 osmosis 5 active transport 6 endocytosis 7 exocytosis A.
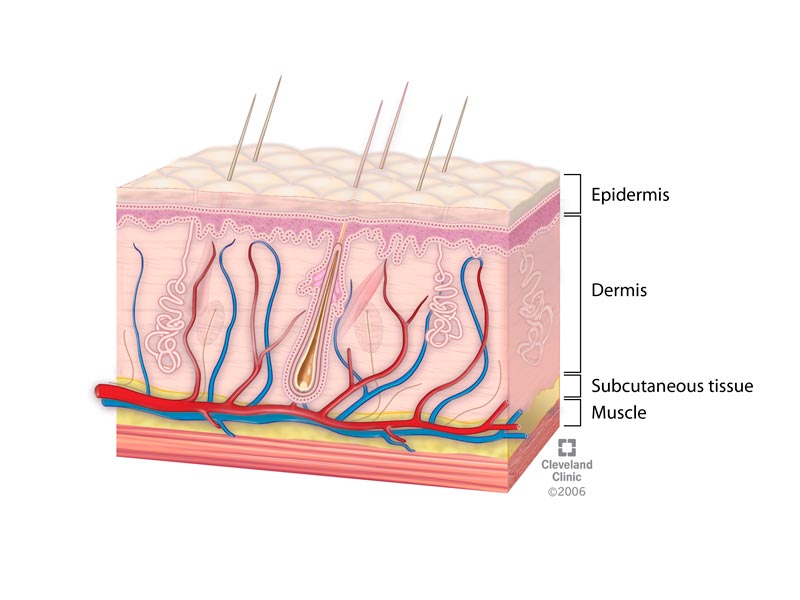
Skin Layers Structure And Function

Skin Diagram And Information About Your Skin Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Psoriasis Skin

No comments for "Describe Three Functions of the Skin"
Post a Comment